California Sea LionZalophus californianus |

Custom Search
|
|
The California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus ) is a coastal sea lion species that lives in western North America. They are very intelligent and adaptable creatures, adapting even to to man-made environments.
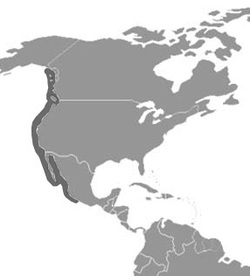
There are 2 recognized subspecies for this species: Zalophus californianus californianus, which lives in coastal waters and the rocky shores of California to Mexico, and Zalophus californianus wollebaeki found in the Galapagos Islands. Some scientists consider these to be separate species. California sea lion males measure approximately 2.2 meters and weigh around 300 kg, while females reach 1.8 meters and weigh much less (about 100 kg). The body and head are slender, with dark brown hair, lighter in some areas, especially in older individuals. Males have a frontal crest, much more prominent than the females. Unlike the Harbor seal, sea lions have ears and move easily on land, raising the body and pushing it forward with the aid of the fins. Their ancient ancestors, like those of killer whales and dolphins used to live on land. California sea lions seek food in the sea, but often come to shore. They can dive to average depths up to 100 m searching for food, with a maximum dive depth between 200 and 275 m. They can reach an estimated speed of 11 km/h.
Their lifespan is between 15 and 25 years in the wild, and over 30 years in captivity. They are gregarious and social animals. A group of California sea lions is called a colony or Rookery.
California sea lions are the species most often found in zoos, it is usually more docile than other sea lions species.They vocalize more frequently than other species of sea lions. The california sea lions is also known as Lobo-Marino Californiano and Californian Sea Lion. The California sea lions are commonly found in marine parks all over the world and often are the stars of the show, and they are even trained by the US Navy for certain military operations. The California sea lion is used by the U.S. Navy for detecting naval mines and enemy divers in the Marine Mammal Program California Sea Lion - Diet They feed mainly on fish but also squid and octopus, which hunt in shallow waters. California sea lions may hunt continuously for up to 30 hours and in each dive they can remain underwater from 3 to 5 minutes. California Sea Lion - Reproduction The mating season is in June, and they join in large groups, on the beaches. At that time, each male defends a territory with a harem of 5 to 20 females moving a lot and emitting loud vocalizations. The gestation period lasts for about a year. The females give birth when they come to shore and mate immediately after, while still breastfeeding. The calf is nursed for several months (usually being weaned at about 11-12 months old), and usually remains with the female until another calf is borne. California Sea Lion females reach sexual maturity at six years of age and males between nine and twelve years. California Sea Lion - Conservation status and main threats According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature, a subspecies that used to live of the coasts of Japan (Zalophus californianus japonicus) is considered extinct and the remaining subspecies are not globally threatened. These are protected animals in their range and numbers have been increasing.
|
Scientific classification
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Carnivora Suborder: Pinnipedia Family: Otariidae Subfamily: Otariinae Genus: Zalophus Species: Z. californianus |