Barbary Sheep (Aoudad)Ammotragus lervia |

Custom Search
|
|
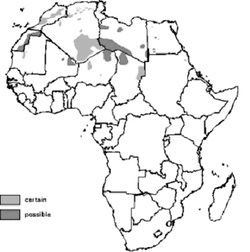
The Aoudad or Barbary Sheep (Ammotragus lervia) can be found in mountainous, rocky desert areas of North Africa, notably in Algeria, Tunisia, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, and Sudan.
These African antelopes are also known by other common names like Arui, Aoudad Sheep, Mouflon a Manchettes (French) and Waddan. There are 6 recognized subspecies. In the past the barbary sheep was widespread in North Africa, inhabiting mountainous and rugged terrains from deserts and semi-deserts to open forests from 650 to 1350 ft (200 to 4100 m). The species was also introduced in into the southern United States in some regions of Texas, New Mexico and California where they were released in the 1950s for sports hunting. The barbary sheep was also introduced into northern Mexico. Barbary Sheep have also been introduced in southern Europe, in some regions of Spain in the 1970s of the and also on Gran Canaria island, which has proved a serious threat to the island's endemic vegetation. They are creatures of crepuscular habits, being particularly active in the early hours of the morning and late afternoon, thus protecting themselves from the high temperatures that are felt during the day in the arid areas that the Barbary Sheep inhabits. They are solitary animals, or who live in small groups wandering during the period of activity in search of food. In captivity, they form a rigid hierarchy with a dominant male, although it is an adult female who directs the movements of the group.
They are robust animals with long horns, which are V-shaped curving backward and reach up to 50 cm. The sexual dimorphism on the Barbary Sheep is pronounced, with males being significantly larger and heavier than females.
These animals can measure between 80 centimeters and 100 meters and weigh between 40 and 140 Kg, depending on sex and time of year. Males also and have a long mane that extends from the neck to forefeet. Barbary Sheep Subspecies / Taxonomy The barbary sheep has 6 subspecies recognized, but their morphological differences are not well defined and there is evidence of hybridization in some areas. So the need for reassessment of these subspecies is urgent. All the subspecies are considered vulnerable, below are the subspecies currently accepted. Atlas Aoudad (Ammotragus lervia lervia - Pallas, 1777) - This subspecies occurs in northern Algeria, northern Tunisia, and Morocco mountainous regions. Egyptian Aoudad (Ammotragus lervia ornata - Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1827) - Found in Egypt in the Western and Eastern Desert, It was thought to be extinct, but was recently rediscovered. Libyan Aoudad (Ammotragus lervia fassini - Lepri, 1930) - This subspecies inhabits only Libya and the extreme southern Tunisia. Aïr Aoudad (Ammotragus lervia angusi - Rothschild, 1921) - Found the in the landlocked Republic of Niger in both the Aïr Massif and Termit Massif). Saharan Aoudad (Ammotragus lervia sahariensis - Rothschild, 1913) - This subspecies of the barbary sheep has the largest range including southern Algeria, southwest Libya, Morocco, Mali, Sudan, Niger, and Mauritania. They have been recently rediscovered in the Western Sahara the disputed territory in the Maghreb region of North Africa. Kordofan Aoudad (Ammotragus lervia blainei - Rothschild, 1913) - At the present time they are probably restricted the east Sudan in the Red Sea hills. It might occur also in southeastern Libya and northeast Chad. This contrasts with their once extensive range spreading from the Red Sea coast to west Sudan. Barbary Sheep Diet They feed on herbaceous plants and other desert plants. They get most of the water they need from dew and the plants they feed. Barbary Sheep Reproduction At the time of reproduction, males fight among themselves for the females. In the fights, males run towards each other and end with a strong head butt. In this species, reproduction occurs normally only once a year, in spring or early winter, when there is more food available. The barbary sheep gestation period is 154 to 161 days, after which only a calf is normally born, weighing about 4 to 5 kilos and is weaned at about 4 months old, becoming increasingly more independent. They reach sexual maturity on average at about 19 months, although in both sexes there are occasions where this happens earlier. Barbary Sheep Conservation status and main threats It is a vulnerable species according to the IUCN. It belongs to the Rev. II of CITES. The Barbary Sheep was once widely distributed throughout the Sahara, but the hunt to obtain meat and leather nearly led to their extinction in many parts of their original range. The major threats to the barbary sheep include poaching and habitat destruction due to several factors like livestock grazing, wood collection and drought, and desertification. In recent years, almost all countries where the Barbary Sheep is found have enacted measures to protect the species in parks and protected areas. It is estimated that in Africa live in the wild between 5000 and 10,000 of these animals. It has been kept in zoos, in which it reproduces relatively well.
|
Scientific classification
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Artiodactyla Family: Bovidae Subfamily: Alcelaphinae Genus: Connochaetes Species: C. gnou |